Heredity and Genetics Notes
|
Offspring—individuals created by parents --offspring get some traits from mother/ some from father --traits cannot “skip a generation” —they just may not be expressed (seen) every time |
 |
Heredity—passing of traits and characteristics from parents to offspring
Trait—genetically determined characteristic
Genetics—study of how traits are passed from parents to offspring
--genetics has become a huge field of study (implications in medicine, agriculture, etc)
What causes traits?
|
Chromosomes—structures that contain information for all traits you have --located in the nucleus of every cell --humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes (or 46 individual chromosomes)
|
|
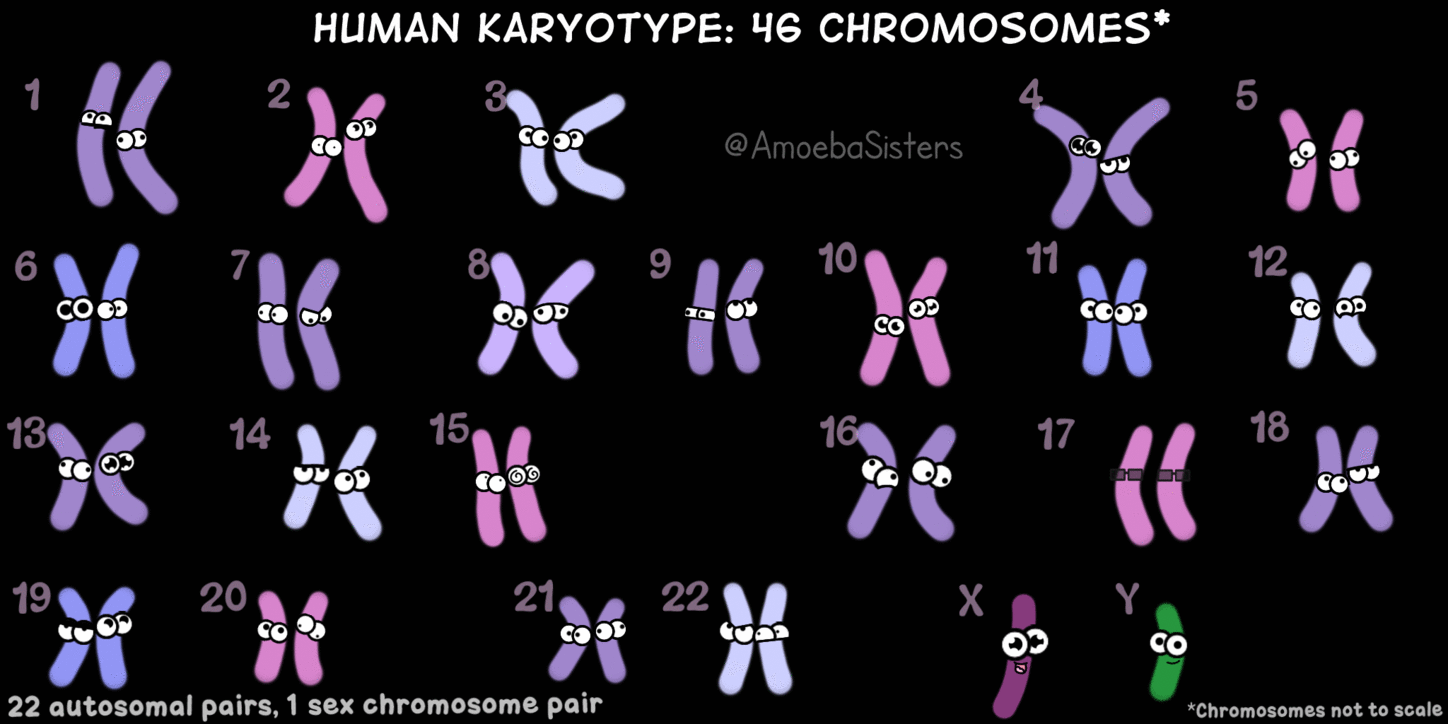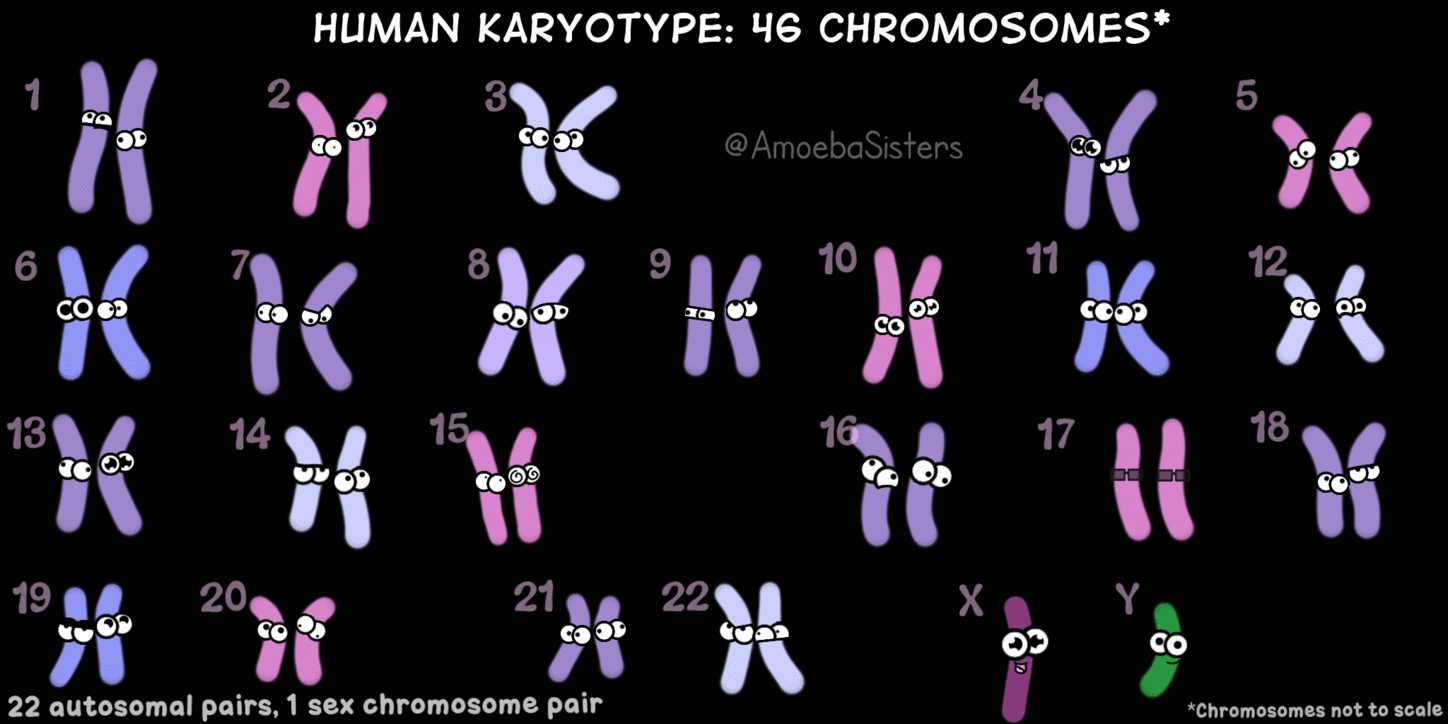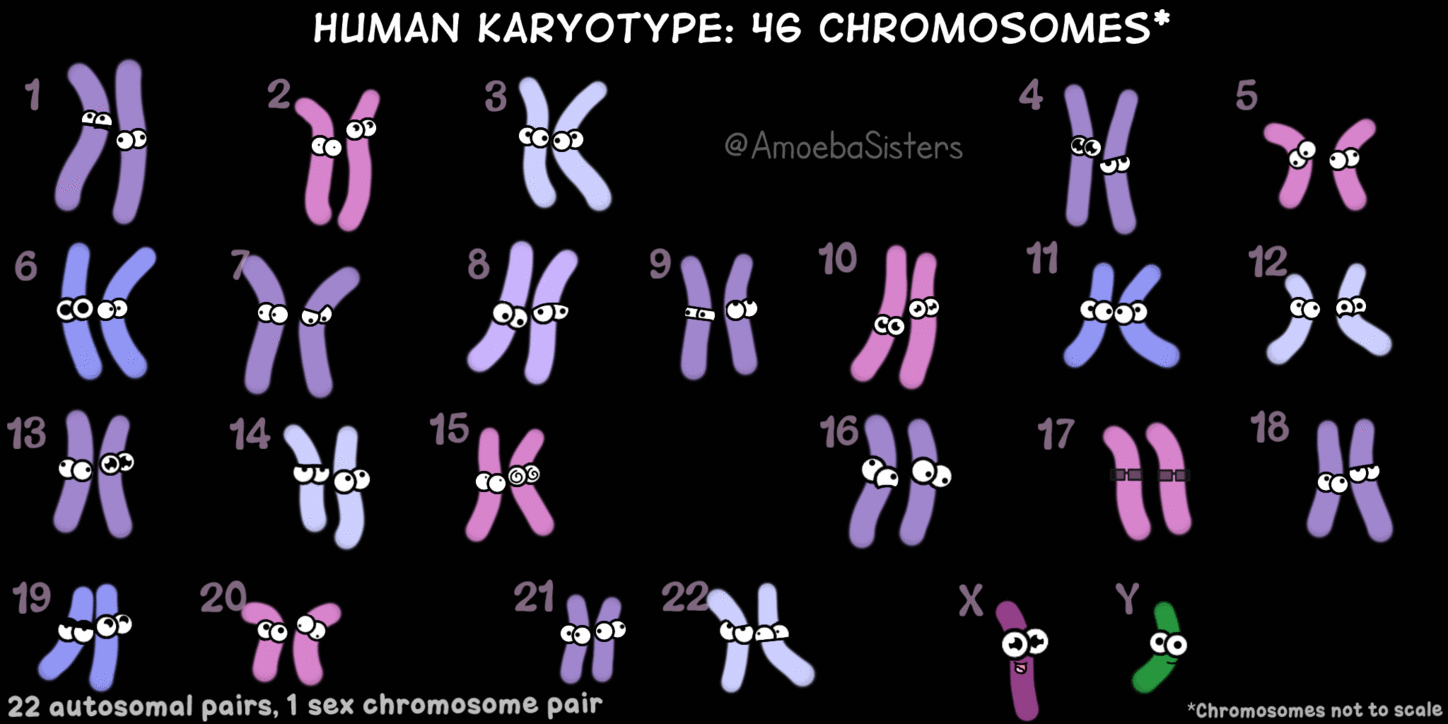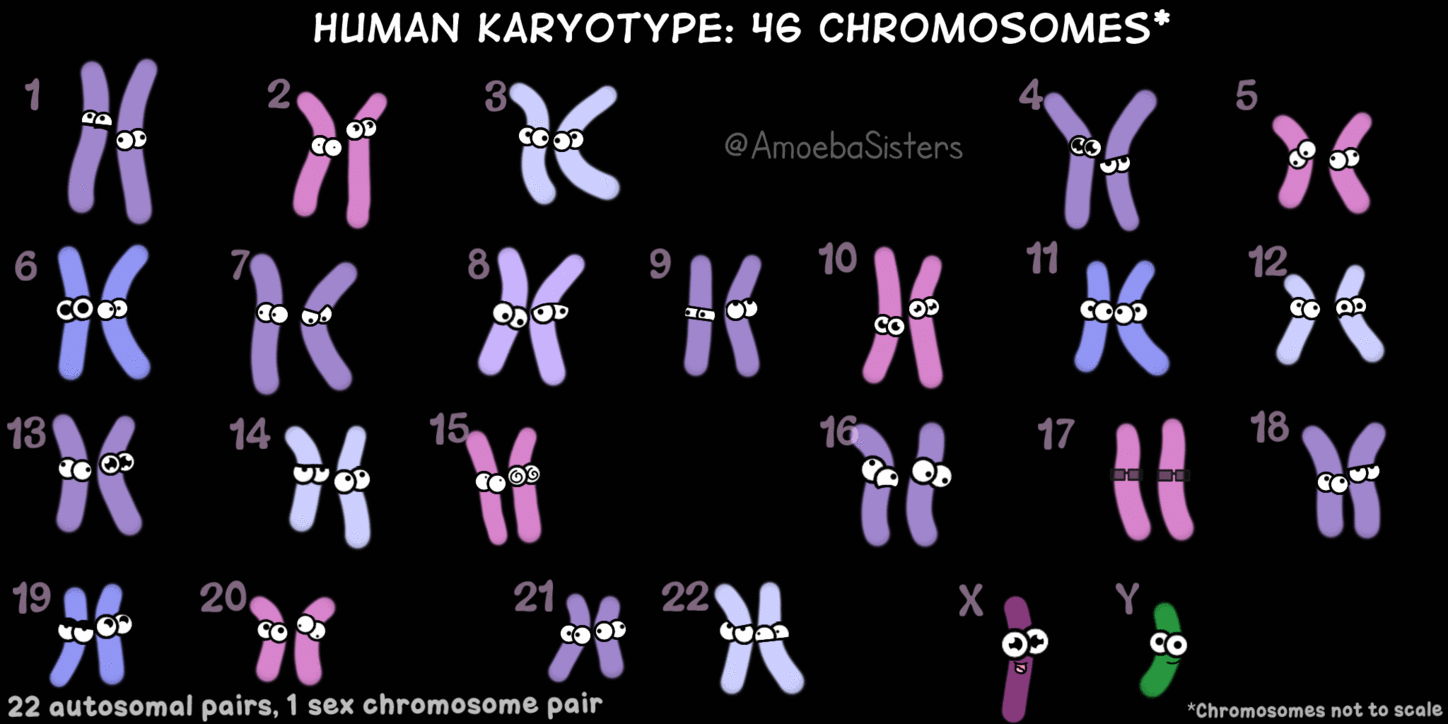
|
|
|
Genes—tiny sections of chromosomes that contain codes for certain traits --a single chromosome can contain thousands of genes --more than 90,000 genes in the human body |
|
|
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)—basic unit of genetic material --makes up genes --shaped is a double helix (like a twisted ladder) --made of 4 different substances called “bases” |
|
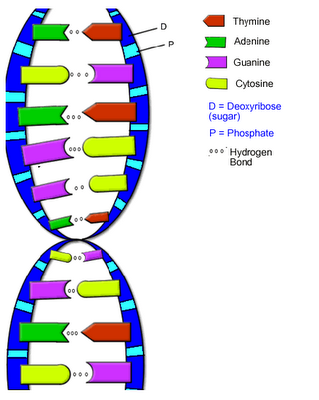 |
4 Bases: Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine
genes of all living things are made of these 4 bases
|
Copying/ making new DNA strands: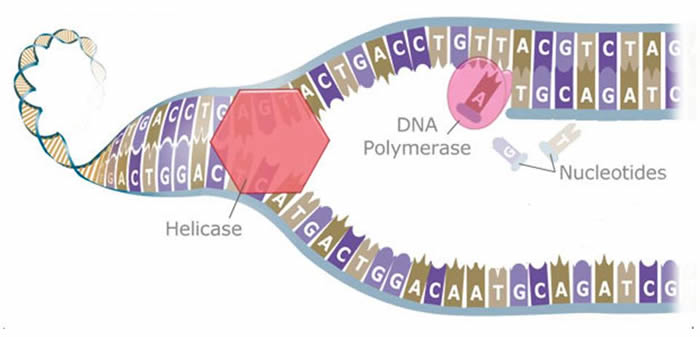
--biggest difference between organisms is the order (sequence) the bases are combined in to form genes (and the number of chromosomes containing genes)
--All living things share certain DNA sequences
--organisms with more sequences in common are more closely related
(humans are more closely related to other mammals than to reptiles, etc)
--humans have over 70 trillion possible combinations
**DNA is the blueprint, the set of instructions, to make all organisms**
